
 |
Serous Detachment of Retina |
 |
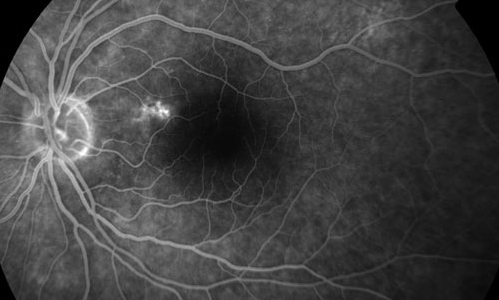
Serous Detachment of Retina | ||
Fluid accumulates under the retina. This separates the retina from the layer beneath, called the choroid. The choroid is the layer that supplies the retina with oxygenated blood. When the retina becomes separated from the choroid, you lose a portion or all of your vision in the affected eye. | ||
| ||
A serous retinal detachment is caused by fluid accumulating underneath the retina, separating it from the retinal pigment epithelium base. This type of retinal detachment occurs because of a systemic illness or condition. | ||
| ||
You may notice you do not have as much peripheral vision in the affected eye. You may notice you have a dark area in your vision on top, bottom, or on a side of your vision. This is often described as a veil or curtain affecting your vision. Sometimes this follows an episode of flashing lights, or new floaters (dark spots). | ||
| ||
A retinal detachment is diagnosed during a dilated eye examination. An optometrist, ophthalmologist, or retina surgeon may find the retina detachment, but only a retina surgeon can repair the damage and restore your vision. | ||
| ||
If the retinal detachment is diagnosed very early, it may be repaired with a laser treatment in a retina clinic. More advanced retinal detachments must be repaired with outpatient surgery. | ||
| ||
There is no know way to prevent this type of retinal detachment. | ||
| ||
 |
 |
|
